0 Comments
0 Shares

Directory
Discover new people, create new connections and make new friends
- Please log in to like, share and comment!
- The Future of Comfort: Ongoing Research and Development in Local Anesthesia with Articaine
The quest for safer, more effective, and more comfortable local anesthesia in dentistry is a continuous pursuit. While articaine hydrochloride has established itself as a valuable anesthetic agent, ongoing research and development are exploring ways to further optimize its use, address potential limitations, and potentially discover even more advanced local anesthetic options.
https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/articaine-hydrochloride-market-2542
One area of ongoing research focuses on minimizing the risk of paresthesia associated with articaine, particularly when used for mandibular nerve blocks. Studies are investigating different injection techniques, needle designs, and anesthetic formulations that might reduce the incidence of this rare but concerning complication.
This includes exploring slower injection rates, lower concentrations in specific scenarios, and alternative block techniques.
Improving the duration of action without increasing the risk of prolonged numbness is another area of interest. Researchers are investigating the use of novel drug delivery systems or additives that could prolong the anesthetic effect of articaine in a predictable and controlled manner, reducing the need for repeat injections during longer procedures while still allowing for a timely return of sensation.
Developing more biocompatible and less toxic formulations of local anesthetics, including articaine, is an ongoing goal. This includes research into alternative preservatives and antioxidants, as well as exploring the potential of naturally derived or bio-inspired anesthetic agents.
Personalized anesthesia based on individual patient factors is a future direction. Research into genetic variations that might influence anesthetic metabolism and response could lead to more tailored anesthetic selection and dosing strategies, optimizing efficacy and minimizing adverse effects.
Advancements in non-invasive or minimally invasive anesthesia delivery systems are also being explored. This includes technologies like transcutaneous patches, iontophoresis (using electrical current to deliver anesthetic through the skin), and needle-free injection devices that could enhance patient comfort and reduce anxiety associated with traditional injections.
The role of imaging guidance in local anesthetic administration is also being investigated. Ultrasound guidance, for example, could potentially improve the accuracy of nerve blocks, reduce the risk of nerve injury, and enhance the predictability of anesthesia.
Research into the pharmacogenomics of local anesthetics, including articaine, aims to understand how individual genetic variations can affect drug metabolism and response. This knowledge could lead to more personalized dosing recommendations and improved safety profiles.
Exploring the synergistic effects of articaine with other analgesic agents is another area of interest. Combining articaine with low doses of other pain-relieving medications could potentially enhance anesthetic efficacy and reduce the overall dose of local anesthetic required.
The future of local anesthesia with articaine, and beyond, is likely to be characterized by a greater emphasis on personalized approaches, minimally invasive delivery, enhanced safety profiles, and optimized duration of action.
Ongoing research and development in these areas hold the promise of even more comfortable, predictable, and effective pain management in dental practice, ultimately benefiting both dental professionals and their patients.The Future of Comfort: Ongoing Research and Development in Local Anesthesia with Articaine The quest for safer, more effective, and more comfortable local anesthesia in dentistry is a continuous pursuit. While articaine hydrochloride has established itself as a valuable anesthetic agent, ongoing research and development are exploring ways to further optimize its use, address potential limitations, and potentially discover even more advanced local anesthetic options. https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/articaine-hydrochloride-market-2542 One area of ongoing research focuses on minimizing the risk of paresthesia associated with articaine, particularly when used for mandibular nerve blocks. Studies are investigating different injection techniques, needle designs, and anesthetic formulations that might reduce the incidence of this rare but concerning complication. This includes exploring slower injection rates, lower concentrations in specific scenarios, and alternative block techniques. Improving the duration of action without increasing the risk of prolonged numbness is another area of interest. Researchers are investigating the use of novel drug delivery systems or additives that could prolong the anesthetic effect of articaine in a predictable and controlled manner, reducing the need for repeat injections during longer procedures while still allowing for a timely return of sensation. Developing more biocompatible and less toxic formulations of local anesthetics, including articaine, is an ongoing goal. This includes research into alternative preservatives and antioxidants, as well as exploring the potential of naturally derived or bio-inspired anesthetic agents. Personalized anesthesia based on individual patient factors is a future direction. Research into genetic variations that might influence anesthetic metabolism and response could lead to more tailored anesthetic selection and dosing strategies, optimizing efficacy and minimizing adverse effects. Advancements in non-invasive or minimally invasive anesthesia delivery systems are also being explored. This includes technologies like transcutaneous patches, iontophoresis (using electrical current to deliver anesthetic through the skin), and needle-free injection devices that could enhance patient comfort and reduce anxiety associated with traditional injections. The role of imaging guidance in local anesthetic administration is also being investigated. Ultrasound guidance, for example, could potentially improve the accuracy of nerve blocks, reduce the risk of nerve injury, and enhance the predictability of anesthesia. Research into the pharmacogenomics of local anesthetics, including articaine, aims to understand how individual genetic variations can affect drug metabolism and response. This knowledge could lead to more personalized dosing recommendations and improved safety profiles. Exploring the synergistic effects of articaine with other analgesic agents is another area of interest. Combining articaine with low doses of other pain-relieving medications could potentially enhance anesthetic efficacy and reduce the overall dose of local anesthetic required. The future of local anesthesia with articaine, and beyond, is likely to be characterized by a greater emphasis on personalized approaches, minimally invasive delivery, enhanced safety profiles, and optimized duration of action. Ongoing research and development in these areas hold the promise of even more comfortable, predictable, and effective pain management in dental practice, ultimately benefiting both dental professionals and their patients.WWW.MARKETRESEARCHFUTURE.COMArticaine Hydrochloride Market Size, Growth and Forecast – 2032 | MRFRArticaine Hydrochloride Market to register 9.10% CAGR and to reach USD 3.27 Billion by 2032. Articaine Hydrochloride Market Research Report by Application, End User and Region | Articaine Hydrochloride Industry0 Comments 0 Shares - 0 Comments 0 Shares
-
- Synthetic Solutions for Sight Restoration: The Promise of Keratoprosthesis and Bioengineered Tissues
For many individuals suffering from severe corneal damage or disease, traditional corneal transplantation using donor tissue has been the primary treatment option. However, limitations in donor availability and the risk of rejection have spurred the exploration of innovative alternatives "beyond transplants." The realm of "artificial corneas," also known as keratoprosthesis, and bioengineered corneal tissues holds immense promise for restoring sight in cases where traditional transplantation is not feasible or has a high risk of failure.
https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/corneal-implants-market-43467
Keratoprosthesis (KPro) involves the surgical implantation of a synthetic device to replace a damaged or opaque cornea. Unlike traditional transplants that rely on biological tissue, KPros are made from biocompatible materials such as polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) or titanium. These devices typically consist of a central optical cylinder that provides a clear visual axis and a peripheral skirt that integrates with the surrounding host corneal tissue.
While KPros have been used for decades, advancements in their design and surgical techniques have significantly improved outcomes. Modern KPros are designed to minimize complications such as glaucoma, infection, and device extrusion. Innovations include improved integration with host tissue, better biocompatibility of materials, and enhanced optical quality. KPros offer a lifeline for patients with conditions like multiple failed corneal transplants, severe ocular surface disease, or certain autoimmune disorders that make traditional transplantation high-risk.
Another exciting area, "beyond transplants," is the development of bioengineered corneal tissues. Researchers are working on creating biosynthetic corneas in the laboratory using materials like collagen, the main structural component of the natural cornea. These bioengineered corneas aim to mimic the natural cornea's structure and function, potentially reducing the risk of rejection and providing a readily available source of transplant tissue.
Several approaches are being explored in bioengineering corneas. One method involves using decellularized animal corneas, where all cellular material is removed, leaving behind a collagen scaffold that can then be repopulated with the patient's cells or integrated into the host tissue. Another approach involves creating entirely synthetic collagen-based scaffolds that can support cell growth and tissue regeneration.
The potential benefits of artificial and bioengineered corneas are significant. They could overcome the limitations of donor tissue availability, reduce the risk of immune rejection, and potentially offer customized solutions for individual patient needs. For individuals with conditions that have historically had poor outcomes with traditional transplantation, these innovative approaches offer a beacon of hope for vision restoration.
While the field of artificial and bioengineered corneas is rapidly advancing, challenges remain. Long-term biocompatibility, achieving seamless integration with host tissue, and ensuring optimal optical quality are ongoing areas of research. However, the progress made so far demonstrates the immense potential of these approaches to move "beyond transplants" and revolutionize the treatment of severe corneal disease, ultimately "exploring the innovative realm of artificial corneas" to restore sight for countless individuals.
In conclusion, "the latest advances in corneal implants" are truly opening "a new window to the world" for individuals with corneal disease. Breakthroughs in biocompatible and bioengineered materials, minimally invasive surgical techniques, and sophisticated implant designs are offering more options, better outcomes, and a brighter future for vision restoration. These innovations are illuminating the path to sight for countless individuals who were once faced with significant visual impairment.Synthetic Solutions for Sight Restoration: The Promise of Keratoprosthesis and Bioengineered Tissues For many individuals suffering from severe corneal damage or disease, traditional corneal transplantation using donor tissue has been the primary treatment option. However, limitations in donor availability and the risk of rejection have spurred the exploration of innovative alternatives "beyond transplants." The realm of "artificial corneas," also known as keratoprosthesis, and bioengineered corneal tissues holds immense promise for restoring sight in cases where traditional transplantation is not feasible or has a high risk of failure. https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/corneal-implants-market-43467 Keratoprosthesis (KPro) involves the surgical implantation of a synthetic device to replace a damaged or opaque cornea. Unlike traditional transplants that rely on biological tissue, KPros are made from biocompatible materials such as polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) or titanium. These devices typically consist of a central optical cylinder that provides a clear visual axis and a peripheral skirt that integrates with the surrounding host corneal tissue. While KPros have been used for decades, advancements in their design and surgical techniques have significantly improved outcomes. Modern KPros are designed to minimize complications such as glaucoma, infection, and device extrusion. Innovations include improved integration with host tissue, better biocompatibility of materials, and enhanced optical quality. KPros offer a lifeline for patients with conditions like multiple failed corneal transplants, severe ocular surface disease, or certain autoimmune disorders that make traditional transplantation high-risk. Another exciting area, "beyond transplants," is the development of bioengineered corneal tissues. Researchers are working on creating biosynthetic corneas in the laboratory using materials like collagen, the main structural component of the natural cornea. These bioengineered corneas aim to mimic the natural cornea's structure and function, potentially reducing the risk of rejection and providing a readily available source of transplant tissue. Several approaches are being explored in bioengineering corneas. One method involves using decellularized animal corneas, where all cellular material is removed, leaving behind a collagen scaffold that can then be repopulated with the patient's cells or integrated into the host tissue. Another approach involves creating entirely synthetic collagen-based scaffolds that can support cell growth and tissue regeneration. The potential benefits of artificial and bioengineered corneas are significant. They could overcome the limitations of donor tissue availability, reduce the risk of immune rejection, and potentially offer customized solutions for individual patient needs. For individuals with conditions that have historically had poor outcomes with traditional transplantation, these innovative approaches offer a beacon of hope for vision restoration. While the field of artificial and bioengineered corneas is rapidly advancing, challenges remain. Long-term biocompatibility, achieving seamless integration with host tissue, and ensuring optimal optical quality are ongoing areas of research. However, the progress made so far demonstrates the immense potential of these approaches to move "beyond transplants" and revolutionize the treatment of severe corneal disease, ultimately "exploring the innovative realm of artificial corneas" to restore sight for countless individuals. In conclusion, "the latest advances in corneal implants" are truly opening "a new window to the world" for individuals with corneal disease. Breakthroughs in biocompatible and bioengineered materials, minimally invasive surgical techniques, and sophisticated implant designs are offering more options, better outcomes, and a brighter future for vision restoration. These innovations are illuminating the path to sight for countless individuals who were once faced with significant visual impairment.WWW.MARKETRESEARCHFUTURE.COMCorneal Implants Market Size, Trends, Growth Report 2035 | MRFRCorneal Implants Market 2025, Industry to reach 5.1 USD billion, at a 3.82% CAGR by driving size, share, top company analysis, segments research, trends and forecast to 2035.0 Comments 0 Shares - Êtes-vous à la recherche d’un interlocuteur intelligent et sans tracas ? Ne cherchez pas plus loin que ChatGPT Francais - ChatGPTxOnline ! Ce chatbot IA de pointe offre une expérience de chat engageante et transparente sans aucun besoin d’inscription ni de frais.
ChatGPT Francais est conçu pour être votre compagnon virtuel incontournable, disponible à tout moment et en tout lieu. Que vous ayez besoin d’aide, que vous souhaitiez lancer une conversation ou simplement rechercher des informations, ce chatbot alimenté par l’IA est là pour vous aider.
Utilisez ici : https://chatgptfrancais.org/
#chatgptfrancais #chatgptgratuit #chatgpt #francais #france #chatgptenligne #chatgptai #chatbot #chatai
Êtes-vous à la recherche d’un interlocuteur intelligent et sans tracas ? Ne cherchez pas plus loin que ChatGPT Francais - ChatGPTxOnline ! Ce chatbot IA de pointe offre une expérience de chat engageante et transparente sans aucun besoin d’inscription ni de frais. ChatGPT Francais est conçu pour être votre compagnon virtuel incontournable, disponible à tout moment et en tout lieu. Que vous ayez besoin d’aide, que vous souhaitiez lancer une conversation ou simplement rechercher des informations, ce chatbot alimenté par l’IA est là pour vous aider. Utilisez ici : https://chatgptfrancais.org/ #chatgptfrancais #chatgptgratuit #chatgpt #francais #france #chatgptenligne #chatgptai #chatbot #chatai0 Comments 0 Shares - Hope on the Horizon: Advances and Emerging Therapies for Breathing Disorders
The field of respiratory medicine is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and the development of innovative therapies offering new hope for individuals living with various breathing disorders. From targeted biological treatments to advanced airway management techniques, the future of respiratory care is promising.
https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/breathing-disorders-treatment-market-1575
Biologics are revolutionizing the treatment of severe asthma and other inflammatory respiratory conditions. These medications are engineered proteins that target specific molecules or pathways involved in the inflammatory process.
For severe allergic asthma, anti-IgE biologics have been available for some time, and newer biologics targeting interleukins (such as IL-5, IL-4, and IL-13) have shown significant efficacy in reducing exacerbations and improving lung function in patients with eosinophilic asthma and other severe asthma phenotypes. Research is ongoing to identify and target other inflammatory pathways in asthma and COPD.
Targeted therapies for pulmonary fibrosis are also advancing. While pirfenidone and nintedanib have provided some benefit, researchers are exploring new medications that target specific pathways involved in lung scarring, with the hope of slowing or even reversing the progression of this debilitating disease.
Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction (BLVR) techniques offer less invasive alternatives to traditional lung volume reduction surgery for select patients with severe emphysema. These procedures involve placing valves or coils in the airways to collapse the most diseased parts of the lung, allowing healthier lung tissue to expand and improve breathing.
Airway stents are being used increasingly to maintain the patency of airways narrowed by tumors, strictures, or other conditions. Newer stent designs aim to be more biocompatible and less prone to complications.
Liquid ventilation, a technique involving filling the lungs with a perfluorocarbon liquid to improve oxygenation and ventilation, is being explored for specific critical respiratory conditions.
High-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) therapy is gaining wider use for providing oxygen and respiratory support in various settings, offering benefits over traditional oxygen delivery methods in some patients with respiratory distress.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being applied to respiratory medicine in areas such as early disease detection, personalized treatment recommendations, and prediction of exacerbations.
Gene therapy holds long-term potential for genetic respiratory diseases like cystic fibrosis, with ongoing research focused on developing safe and effective ways to deliver functional genes to lung cells.
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs are becoming more sophisticated, incorporating virtual reality and telerehabilitation to improve accessibility and engagement.
Research into the microbiome of the respiratory tract is revealing its potential role in the development and progression of breathing disorders, opening avenues for novel therapeutic interventions targeting the microbial environment.
Early detection and prevention strategies are also crucial areas of focus. Efforts are underway to identify individuals at high risk for developing breathing disorders and to implement interventions that can prevent or delay disease onset.
The landscape of respiratory medicine is dynamic, with continuous innovation driving the development of new and improved therapies for breathing disorders. These advances offer hope for better symptom control, improved quality of life, and potentially disease modification for millions of individuals affected by these conditions worldwide.
Continued research and collaboration among scientists, clinicians, and patients are essential to translate these promising developments into tangible benefits for those who struggle to breathe.Hope on the Horizon: Advances and Emerging Therapies for Breathing Disorders The field of respiratory medicine is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and the development of innovative therapies offering new hope for individuals living with various breathing disorders. From targeted biological treatments to advanced airway management techniques, the future of respiratory care is promising. https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/breathing-disorders-treatment-market-1575 Biologics are revolutionizing the treatment of severe asthma and other inflammatory respiratory conditions. These medications are engineered proteins that target specific molecules or pathways involved in the inflammatory process. For severe allergic asthma, anti-IgE biologics have been available for some time, and newer biologics targeting interleukins (such as IL-5, IL-4, and IL-13) have shown significant efficacy in reducing exacerbations and improving lung function in patients with eosinophilic asthma and other severe asthma phenotypes. Research is ongoing to identify and target other inflammatory pathways in asthma and COPD. Targeted therapies for pulmonary fibrosis are also advancing. While pirfenidone and nintedanib have provided some benefit, researchers are exploring new medications that target specific pathways involved in lung scarring, with the hope of slowing or even reversing the progression of this debilitating disease. Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction (BLVR) techniques offer less invasive alternatives to traditional lung volume reduction surgery for select patients with severe emphysema. These procedures involve placing valves or coils in the airways to collapse the most diseased parts of the lung, allowing healthier lung tissue to expand and improve breathing. Airway stents are being used increasingly to maintain the patency of airways narrowed by tumors, strictures, or other conditions. Newer stent designs aim to be more biocompatible and less prone to complications. Liquid ventilation, a technique involving filling the lungs with a perfluorocarbon liquid to improve oxygenation and ventilation, is being explored for specific critical respiratory conditions. High-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) therapy is gaining wider use for providing oxygen and respiratory support in various settings, offering benefits over traditional oxygen delivery methods in some patients with respiratory distress. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being applied to respiratory medicine in areas such as early disease detection, personalized treatment recommendations, and prediction of exacerbations. Gene therapy holds long-term potential for genetic respiratory diseases like cystic fibrosis, with ongoing research focused on developing safe and effective ways to deliver functional genes to lung cells. Pulmonary rehabilitation programs are becoming more sophisticated, incorporating virtual reality and telerehabilitation to improve accessibility and engagement. Research into the microbiome of the respiratory tract is revealing its potential role in the development and progression of breathing disorders, opening avenues for novel therapeutic interventions targeting the microbial environment. Early detection and prevention strategies are also crucial areas of focus. Efforts are underway to identify individuals at high risk for developing breathing disorders and to implement interventions that can prevent or delay disease onset. The landscape of respiratory medicine is dynamic, with continuous innovation driving the development of new and improved therapies for breathing disorders. These advances offer hope for better symptom control, improved quality of life, and potentially disease modification for millions of individuals affected by these conditions worldwide. Continued research and collaboration among scientists, clinicians, and patients are essential to translate these promising developments into tangible benefits for those who struggle to breathe.WWW.MARKETRESEARCHFUTURE.COMBreathing Disorders & Treatment Market Research Report-Global Forecast To 2032 | MRFRBreathing Disorders Treatment Market is anticipated to register a 7.28% CAGR during the Projected Period, Global Breathing Disorders Treatment Market categorizes the Worldwide Market by Type and Region | Breathing Disorders Treatment Industry0 Comments 0 Shares - The depth of the under bench basin really affects how easy it is to use. Deeper sinks are great for handling big pots and pans, which helps keep splashes to a minimum when you're washing a lot of dishes.
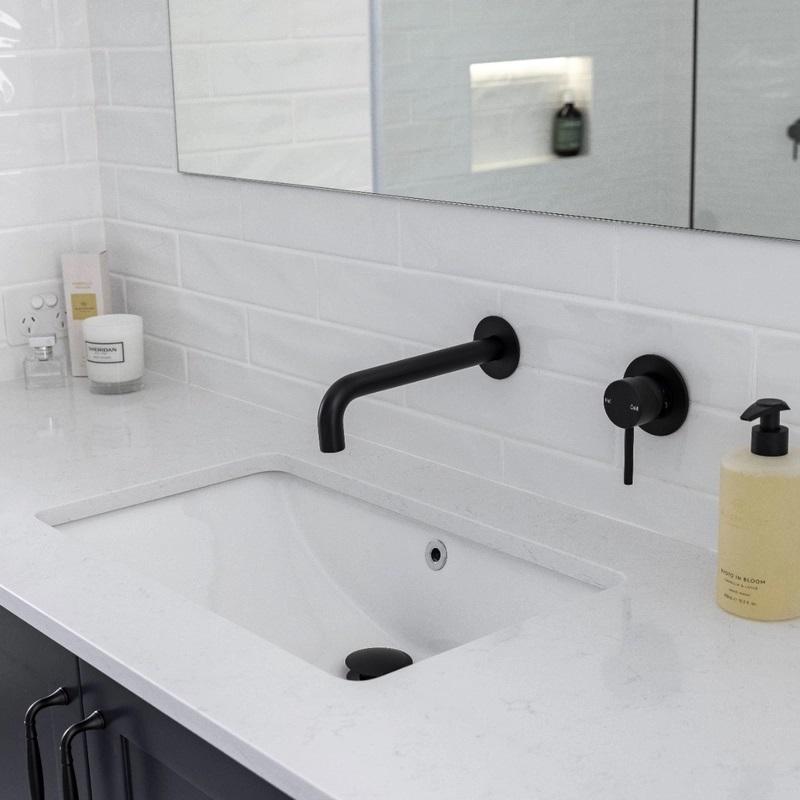
https://aussomeinsights.mystrikingly.com/blog/the-what-s-and-how-s-of-buying-an-undermounted-sinkThe depth of the under bench basin really affects how easy it is to use. Deeper sinks are great for handling big pots and pans, which helps keep splashes to a minimum when you're washing a lot of dishes. https://aussomeinsights.mystrikingly.com/blog/the-what-s-and-how-s-of-buying-an-undermounted-sink0 Comments 0 Shares - Unlock Greater Independence with the Latest Self-Injection Technologies
For individuals managing chronic conditions that require regular injectable medications, the act of self-injection can sometimes feel like a tether, a constant reminder of their dependence on treatment. However, the latest advancements in self-injection technologies are working to shift this paradigm, offering tools that empower users with greater independence, convenience, and control over their medication administration. These innovations are designed to simplify the process, reduce anxiety, and seamlessly integrate treatment into daily life.
https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/self-injection-device-market-43501
One of the key ways self-injection technologies are fostering independence is through enhanced ease of use. Many of the newer devices feature ergonomic designs that are easier to grip and handle, particularly for individuals with dexterity limitations or arthritis. Automated injection mechanisms reduce the need for precise manual movements, allowing users to administer their medication with greater confidence and less reliance on assistance from others. This newfound ease of use can be particularly empowering for those who previously struggled with the injection process.
Smart autoinjectors are at the forefront of this movement towards greater independence. These devices often feature pre-filled cartridges or pre-measured doses, eliminating the need for manual drawing up of medication. With the press of a button, the device automatically inserts the needle to the correct depth and delivers the medication at a controlled rate. Some even provide audible or visual cues to confirm successful injection. This automation not only simplifies the process but also reduces the potential for dosing errors, further enhancing user confidence and independence.
Connectivity is another crucial aspect of these technologies that promotes self-management. Many smart self-injection devices seamlessly integrate with mobile apps via Bluetooth. These apps can provide reminders for scheduled injections, track injection history, and even guide users on proper injection technique and site rotation. This digital support system puts users in control of their treatment schedule and provides valuable insights into their adherence patterns, fostering a greater sense of ownership over their health.
Furthermore, some of the latest self-injection technologies are designed with discretion in mind. Smaller, more discreet devices allow users to administer their medication more privately and conveniently, without drawing undue attention. This can be particularly important for individuals who feel self-conscious about their injections and want to maintain a sense of normalcy in their social and professional lives.
The reduction of injection anxiety is another significant factor contributing to greater independence. The fear of needles and the discomfort associated with injections can be a major barrier to self-administration for many individuals. Newer self-injection devices often feature ultra-fine needles and mechanisms that minimize the sensation of pain. Some devices also offer features like hidden needles or slower injection speeds to further reduce anxiety and improve the overall injection experience, making users more likely to self-administer consistently and independently.
Moreover, the data tracking capabilities of smart self-injection devices can empower users during consultations with their healthcare providers. By having a readily available log of their injections, including dates, times, and doses, patients can have more informed and productive discussions about their treatment progress and any challenges they may be facing. This data-driven approach fosters a greater sense of collaboration and shared decision-making, further enhancing the patient's independence in managing their condition.
In conclusion, the latest self-injection technologies are playing a vital role in unlocking greater independence for individuals managing chronic conditions. By offering enhanced ease of use, automation, connectivity, discretion, and reduced anxiety, these innovative devices empower users to take control of their medication administration and seamlessly integrate treatment into their daily lives. This newfound independence can lead to improved adherence, greater confidence, and a significantly enhanced overall quality of life. As these technologies continue to evolve, they promise to further empower individuals to manage their health on their own terms.Unlock Greater Independence with the Latest Self-Injection Technologies For individuals managing chronic conditions that require regular injectable medications, the act of self-injection can sometimes feel like a tether, a constant reminder of their dependence on treatment. However, the latest advancements in self-injection technologies are working to shift this paradigm, offering tools that empower users with greater independence, convenience, and control over their medication administration. These innovations are designed to simplify the process, reduce anxiety, and seamlessly integrate treatment into daily life. https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/self-injection-device-market-43501 One of the key ways self-injection technologies are fostering independence is through enhanced ease of use. Many of the newer devices feature ergonomic designs that are easier to grip and handle, particularly for individuals with dexterity limitations or arthritis. Automated injection mechanisms reduce the need for precise manual movements, allowing users to administer their medication with greater confidence and less reliance on assistance from others. This newfound ease of use can be particularly empowering for those who previously struggled with the injection process. Smart autoinjectors are at the forefront of this movement towards greater independence. These devices often feature pre-filled cartridges or pre-measured doses, eliminating the need for manual drawing up of medication. With the press of a button, the device automatically inserts the needle to the correct depth and delivers the medication at a controlled rate. Some even provide audible or visual cues to confirm successful injection. This automation not only simplifies the process but also reduces the potential for dosing errors, further enhancing user confidence and independence. Connectivity is another crucial aspect of these technologies that promotes self-management. Many smart self-injection devices seamlessly integrate with mobile apps via Bluetooth. These apps can provide reminders for scheduled injections, track injection history, and even guide users on proper injection technique and site rotation. This digital support system puts users in control of their treatment schedule and provides valuable insights into their adherence patterns, fostering a greater sense of ownership over their health. Furthermore, some of the latest self-injection technologies are designed with discretion in mind. Smaller, more discreet devices allow users to administer their medication more privately and conveniently, without drawing undue attention. This can be particularly important for individuals who feel self-conscious about their injections and want to maintain a sense of normalcy in their social and professional lives. The reduction of injection anxiety is another significant factor contributing to greater independence. The fear of needles and the discomfort associated with injections can be a major barrier to self-administration for many individuals. Newer self-injection devices often feature ultra-fine needles and mechanisms that minimize the sensation of pain. Some devices also offer features like hidden needles or slower injection speeds to further reduce anxiety and improve the overall injection experience, making users more likely to self-administer consistently and independently. Moreover, the data tracking capabilities of smart self-injection devices can empower users during consultations with their healthcare providers. By having a readily available log of their injections, including dates, times, and doses, patients can have more informed and productive discussions about their treatment progress and any challenges they may be facing. This data-driven approach fosters a greater sense of collaboration and shared decision-making, further enhancing the patient's independence in managing their condition. In conclusion, the latest self-injection technologies are playing a vital role in unlocking greater independence for individuals managing chronic conditions. By offering enhanced ease of use, automation, connectivity, discretion, and reduced anxiety, these innovative devices empower users to take control of their medication administration and seamlessly integrate treatment into their daily lives. This newfound independence can lead to improved adherence, greater confidence, and a significantly enhanced overall quality of life. As these technologies continue to evolve, they promise to further empower individuals to manage their health on their own terms.WWW.MARKETRESEARCHFUTURE.COMSelf Injection Device Market Size, Growth Report 2035 | MRFRSelf Injection Device Market 2025, Industry to reach USD 10.5 Billion, at a 7.15% CAGR by growing size, share, top company analysis, segments research, trends and forecast to 20350 Comments 0 Shares - Top-Quality Electrical Equipment for Campervans in Ireland
Power your adventures with premium #electrical_campervan_equipment_in_Ireland from Nolan Camper Supplies. From inverters and batteries to lighting and wiring kits, we provide everything you need for a safe and efficient campervan electrical setup.
https://nolancampersupplies.ie/product-category/electrical/Top-Quality Electrical Equipment for Campervans in Ireland Power your adventures with premium #electrical_campervan_equipment_in_Ireland from Nolan Camper Supplies. From inverters and batteries to lighting and wiring kits, we provide everything you need for a safe and efficient campervan electrical setup. https://nolancampersupplies.ie/product-category/electrical/NOLANCAMPERSUPPLIES.IEElectrical Campervan Accessories | Electrical Camper Equipment suppliesGet the best camper van electrical supplies. From wiring to equipment, find for a reliable electrical system in your campervan. Quality supplies available.0 Comments 0 Shares
© 2025 Soboz · English